Materi SMBD
" Sistem Manajemen Basis Data "
Pengertian Manajemen Basis data pada SIG yaitu Greader merupakan wadah yang terdiri dari kolom dan tempat menyimpan kumpulan data atau informasi. Sebuah basis data dapat diakses dan dikelola menggunakan software pengelola basis data yaitu Data Base Manajemen system.
- Input data yaitu langkah pengkodean data menjadi suatu bentuk yang dapat dipahami komputer dan menuliskannya kedalam basis data SIG. Terdapat dua type data saja yang dapat dimasukan kedalam SIG yaitu data spasial dan non-spasial. Untuk menampilkan lokasi geografis maka tipe yang digunakan adalah data spasial. Sedangkan untuk menampilkan gambaran atau deskripsi seperti nama jalan, nama hutan dan lain sebagainya maka tipe yang digunakan adalah data non-spasial.
- Manajemen data yang berisi fungsi untuk memanggil dan menyimpan data. Data yang diinput diolah sedemikian rupa didalam sistem database. Basis data memiliki model data yaitu organisasi konseptual yang berada dalam basis data. Model data terdiri dari model hirarki, model jaringan dan model data relasional.
- Manipulasi dan analisis data yang mengolah data semaksimal mungkin untuk mendapatkan informasi dari SIG. Perubahan bentuk dan proses analisis dengan cara membuat penalaran dari data spasial dan non-spasial yang berupa deretan data grafis maupun hubungan data grafis dan atribut.
- Penyajian Data yang merupakan langkah untuk menampilkan informasi dari SIG menjadi bentuk yang diharapkan user. Output data ditampilkan dalam bentuk printing dan softfile. Output dalam format printing atau hardfile berupa tampilan tetap, yang dicetak pada kertas, film fotografik atau material lain. Output dalam softfileditampilkan melalui layar monitor baik berupa teks atau grafik guna melihat hasil analisis sebelum dicetak secara permanen.
- dinat Lokasi
- Nama Lokasi
- Lokasi Topologi
- Curah Hujan
- Jumlah panen padi
- Terdiri dari variabel (tanah), kelas (alluvial) dll
Data non lokasi di lokasi bersangkutan dapat berubah dengan waktu misalnya : data curah hujan bulan Desember akan berbeda beda dengan Bulan Juli.
A.Desain Konseptual :
— A data model is a formal specification for the entities, their attributes and all relationships between the entities for the GIS.
- Bentuknya sederhana
- Mudah melakukan berbagai operasi data.
SIG mampu menggambarkan data geografis sehingga fungsi diatas dapat berjalan dengan baik. Data geografi yang digambarkan oleh SIG berupa.
Data spasial dan informasi geografis saling terhubung oleh SIG mengenai atribut tertentu ada peta. Contohnya yaitu objek titik, garis, atau poligon pada peta. Informasi ini disebut fitur atau ciri – ciri dari atribut yang ditamppakkan secara grafis.
Seiring berkembang pesatnya teknologi kini Manajemen Basis Data sudah menjadi sistem penting bagi SIG . beberapa data yang valid juga mengungkapkan bahwa Manajemen Basis Data memperoleh biaya dari sebagian sistem software sistem informasi geografis. Karena Sistem Informasi Geografis (SIG) dimiliki oleh Manajemen Basis Data dan Sistem Informasi Geografis juga membutuhkan SMDB ini untuk menjalankan fungsi – fungsinya.
Tipe Data :
A. Data Lokasi :
Desain Koseptual;
1. Parts of E-R Model:
• Entities
•
Relationships between entities
•
Attributes of entities or
relationships
2. Types of
normal relationships:
• Belonging to
•
Set and subset relationships
•
Parent-child relationships
Component parts of an
object
3. Rules for identifying entities, relationships, and attributes:
•
A common noun corresponds
to an entity type;
•
A transitive verb corresponds
to a relationship type;
•
An adjective corresponds
to
an attribute type.
— Each entity and its
attribute map into one or more relational tables.
Each
relationship is a regular relationship executed by the relational database query system or a spatial
relationship and if it is not a
standard operation then the indicated operation which usually includes a
complex computation need to be written (using Avenue
Script/Macro Language).
Desain Konseptual Metadata :
—
Metadata is “information about data”: (i) describe the characteristics of
the data (entity and attributes)
using its standard name, and (ii) provide information on its accuracy and its
source and its archiving provision.
—
Important functions of metadata: provide (i) a basic data description of a data set;
(ii) information for data transfer /
sharing; (iii) information for entries into clearinghouses to catalogue the availability of data.
—
Metadata should serve as: (i) a
documentation and data management
tool; (ii) data definition, source
documentation, management and updating,
data archiving and retention requirement; (iii) information to support
database description for spatial data clearing houses.
An example of metadata tables:
Perncanaan DB :
— 1. The quality of information :
|Information is
stored in a database
|Bad construction and
data error will give Garbage instead of Geographic Information System
|What kind of map
projection will be used
|What scale is the
data
| What is the
coverage
|How much attribution
should be included
|What is the
attribute data format
|What is the data
reliability
|How fast is it to be
retrieved
— 2. Information required
for database design:
|A
complete list of data, properly defined and checked
for validity and consistency (from the master data list, E-R data model, and
metadata entries);
|A
list of potential data source (maps, aerial photos, tabular files, digital files) cataloged
and evaluated for accuracy and
completeness (from available data
survey);
|The
list of functional capabilities required from the
GIS (from needs assessment). Such as visualization, spatial analysis, statistical analysis and modeling.
3. Plan fordata sharing :
|Benefits
of data sharing include: (i) the development of much larger database for far less cost; (ii) the development
of more efficient interaction between
public agencies; and (iii) all agencies shared the same up-to-date
database / information.
|Database maintenance requires two efforts:
ongoing user training (how to maintain the database) and user support (who
will be responsible for updating which data).
4. Designingthr Database :
|Most
of databases in GIS software packages are based on the relational database
model;
|Two choices of using data table: as much data in one table or small/compact
data in one table;
|How you will represent the data: point, line, polygon, network, etc.
B. Kontruksi DB :
— Database construction/conversion is the process of building the digital database from the source data - maps and tabular files.
—The
main emphasis is management of the activity and quality assurance / quality control of the converted data.
— Manual
digitizing using a digitizing tablet and cursor tool (puck);
— Scanning (converts
lines and text into series of pixels);
— Raster
to Vector Conversion (convert series of pixels into series of (x,y)
coordinates points), this facility is usually provided
by a GIS software;
— Hybrid solution (overlaying vector format data with an image display tool
• Map graphics represent all of the
features (entities) on a map as points, lines, areas, or pixels;
•
Tabular databases
contain the attribute information which
describe the entities (building, parcel, etc.);
•
A common key (graphics data index) must be established between the map
graphics and the tabular database records to
create a link.
—
Raster Data (pixels)
—
Vector GIS Data
C. Basis Data Relasional :
— Basis Data relasional menggunakan tabel dua dimensi yang terdiri atas
baris dan kolom untuk memberi gambaran sebuah berkas data.
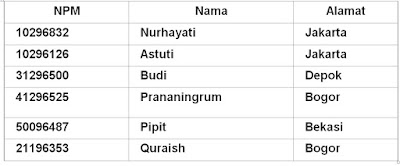
MHS :
MKUL :
NILAI :
Keuntungan Basis Data Relasional :
D. Hybrid & Integrated System :
Pengertian dari Hybrid dan Integrated System yaitu Struktur data vektor dan struktur data raster dapat dipadukan pada suatu sistem dengan melengkapi fasilitas konversi vektor ke raster dan raster ke vektor. Selain itu juga disediakan fungsi -fungsi untuk mengolah masing masing struktur data.
Operasional SIG secara keseluruhan yang terdiri dari SIG software, Image processing, GPS software, Open source component, DBMS system.
Referensi :












Comments
Post a Comment